Transvaginal Mesh: An Overview of a Controversial Medical Device
Transvaginal mesh (TVM) is a medical implant utilized for addressing different pelvic floor disorders experienced by women. Over the past years, this device has become a matter of dispute and legal action due to reported complications and unfavorable outcomes. In the following discussion, we will delve into the subject of transvaginal mesh, examining its applications, associated hazards, legal ramifications, and the ongoing discourse concerning its safety.
Understanding Transvaginal Mesh
Vaginal mesh, commonly referred to as transvaginal mesh or pelvic mesh, is an implantable surgical device composed of synthetic materials like polypropylene. Its main purpose is to address conditions such as pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in women. These conditions occur when the muscles and tissues in the pelvic region weaken or suffer damage, frequently caused by factors such as childbirth, aging, or other related factors.
The Purpose and Procedure of
Transvaginal Mesh
Transvaginal mesh is primarily designed to offer supplementary support to weakened pelvic muscles and tissues. In the procedure, the mesh is surgically implanted via the vagina to reinforce the affected region. Acting as a scaffold, the mesh facilitates tissue growth and aids in restoring regular functionality. Its purpose is to provide enduring support and alleviate the symptoms commonly associated with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and stress urinary incontinence (SUI).
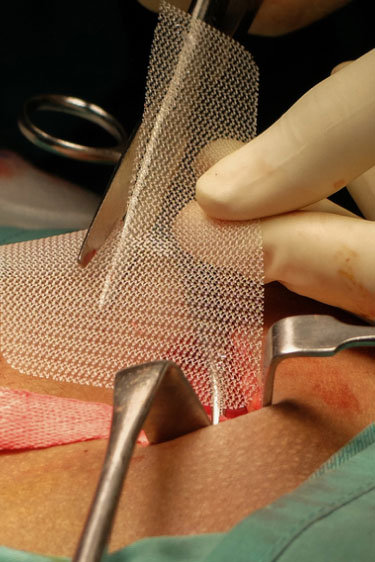
Reported Complications and Concerns After Transvaginal Mesh
However, transvaginal mesh procedures have been associated with a range of complications, leading to numerous lawsuits and widespread concern. Some of the reported complications include:
- Mesh Erosion: In some cases, the mesh can erode or protrude into surrounding tissues or organs, causing pain, discomfort, and infection.
- Infection: The implantation of transvaginal mesh carries a risk of infection, which can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
- Pain and Discomfort: Many women have reported chronic pain and discomfort following transvaginal mesh surgery, affecting their quality of life.
- Mesh Migration and Contraction: The mesh may move from its original position or contract, leading to further complications and the need for additional surgeries.
Legal Actions and Regulatory Responses Against Transvaginal Mesh
With mounting concerns surrounding the complications associated with transvaginal mesh, a substantial wave of lawsuits emerged against the manufacturers of these devices. These legal actions contended that manufacturers did not sufficiently inform patients and healthcare providers about the potential risks connected to it.
In response to the escalating controversy, regulatory authorities in different countries took measures to address the issue. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reclassified transvaginal mesh as a high-risk device, necessitating manufacturers to submit supplementary clinical data that demonstrates its safety and efficacy.
Ongoing Debate and Patient Advocacy Concerning Transvaginal Mesh
The debate surrounding transvaginal mesh remains contentious. Advocacy groups argue that stricter regulations and comprehensive studies are needed to evaluate the safety of these devices thoroughly. They highlight the importance of informed consent and ensuring that patients are fully aware of the potential risks before undergoing any procedure.
On the other hand, some medical professionals believe that when used judiciously in appropriate cases, it can still be a valuable treatment option. They argue that the reported complications may be linked to improper surgical techniques or inadequate training rather than inherent flaws in the device itself.
Safety and Effectiveness of Transvaginal Mesh
The use of transvaginal mesh has ignited intense debates due to its complications and legal implications. While it offers potential relief for women experiencing pelvic floor disorders, it is vital not to disregard the associated risks and potential complications. Healthcare professionals and patients should engage in comprehensive discussions, exploring alternative treatment options and making informed decisions. Ongoing research and regulatory endeavors aim to further evaluate and enhance the safety and effectiveness of transvaginal mesh procedures, with the ultimate goal of ensuring the well-being of women seeking treatment for pelvic floor disorders.
